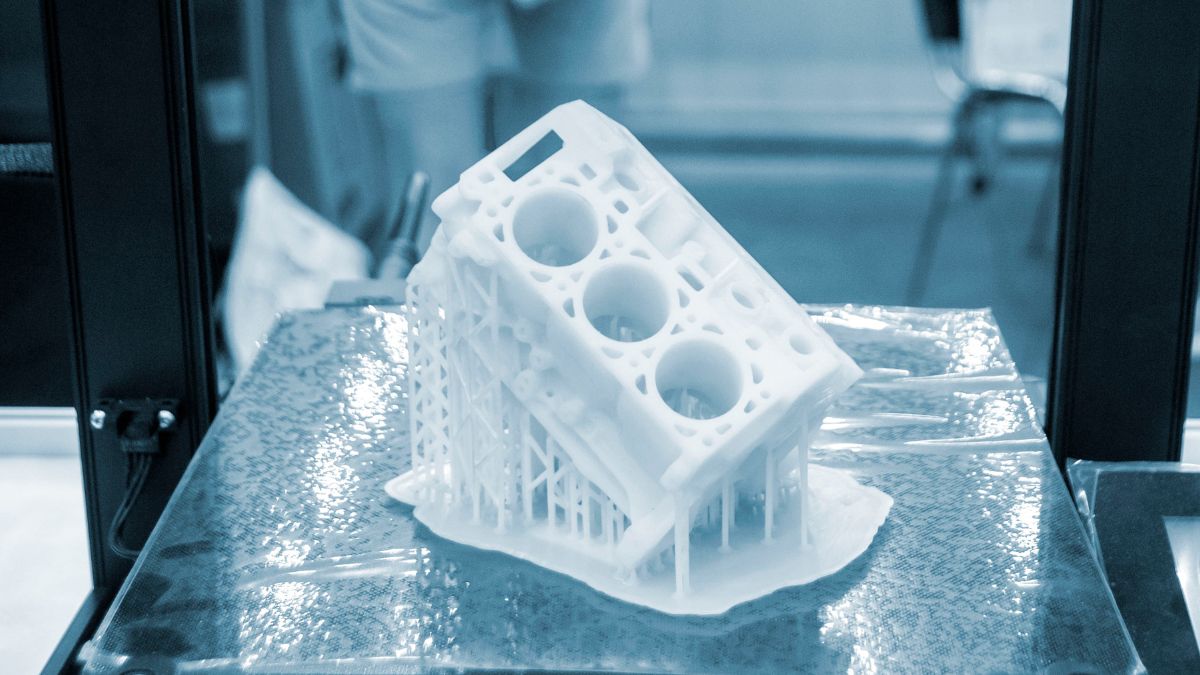
Throughout history, technology has reimagined how products are manufactured. Today, we have innovations like artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) driving sweeping changes in the industry. But it’s 3D printing — a type of additive manufacturing process — that’s proving itself to be truly revolutionary.
Let’s explore the different ways 3D printing is changing the game for manufacturers operating across a diverse cross-section of industries.
How 3D Printing Reshapes Manufacturing
Manufacturers have always valued efficiency. It’s a core tenet of any production workflow. They also value waste reduction, flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and speed.
Traditional manufacturing processes like CNC machining and injection molding can deliver up to a certain extent. But they have limitations.
For one, setup costs are high. They require expensive tooling, and often, the quality of the product is directly correlated with the cost of the machinery — a higher investment results in superior-quality products. This can make competition tough for smaller-scale manufacturers. Plus, production times are also lengthy.
For large-scale manufacturers mass-producing goods, these obstacles are something they can overcome.
But for others, customers demand custom, fit-for-product solutions, something conventional manufacturing processes struggle to deliver without it getting expensive and time-consuming.
The introduction of 3D printing and its evolution into a viable manufacturing option has empowered manufacturers to hold onto the business outcomes they value, while meeting changing customer expectations.
For these reasons, the industry is exploding. In 2023, the additive manufacturing services sector grew 20%. In 2024, it’s expected to expand by an additional 22.7% to reach a market value of $7 billion.
Setup costs are low (in the case of working with manufacturing as a service (MaaS) companies like A3D Manufacturing), and production timelines are fast. 3D printing has become particularly beneficial in industries that require agility, like aerospace, consumer goods, and medicine.
Now, let’s jump into the specifics. Here are five concrete ways 3D printing is rethinking manufacturing across industries from the ground up.
1. Custom Parts and Tools in Industrial Equipment
Industrial equipment often requires highly specialized parts that can be difficult to source. Delays lead to costly downtime as the machine sits idle, waiting for custom tools or replacement parts.
3D printing shortens this process. With on-demand printing, manufacturers can produce custom parts and tools in-house within hours or days instead of waiting for external suppliers. This not only reduces downtime but also improves operational efficiency.
For example, companies can 3D-print jigs, fixtures, and machine tools that meet their specific needs at a fraction of the cost of traditional machining.
In addition, companies become more resilient to global supply chain disruptions and volatile market prices.

2. Personalization in the Medical Industry
3D printing can be used to create patient-specific medical devices — think prosthetics, implants, and surgical guides. Where traditional methods involve long lead times and high costs, 3D printing makes it possible to deliver personalized medical solutions quickly and at a more accessible price point.
For example, prosthetic and orthopedic companies manufacture custom prosthetic limbs based on a patient’s unique anatomy. These devices fit better, function more comfortably, and can be produced much faster than prosthetics made with traditional methods.
Prosthetics are not cheap. A myoelectric arm, which uses a patient’s natural electromyographic signals to move, can cost around $100,000 or more. Even simpler prosthetics like above-knee devices are about $70,000 or so. 3D printing can help alleviate costs for patients.
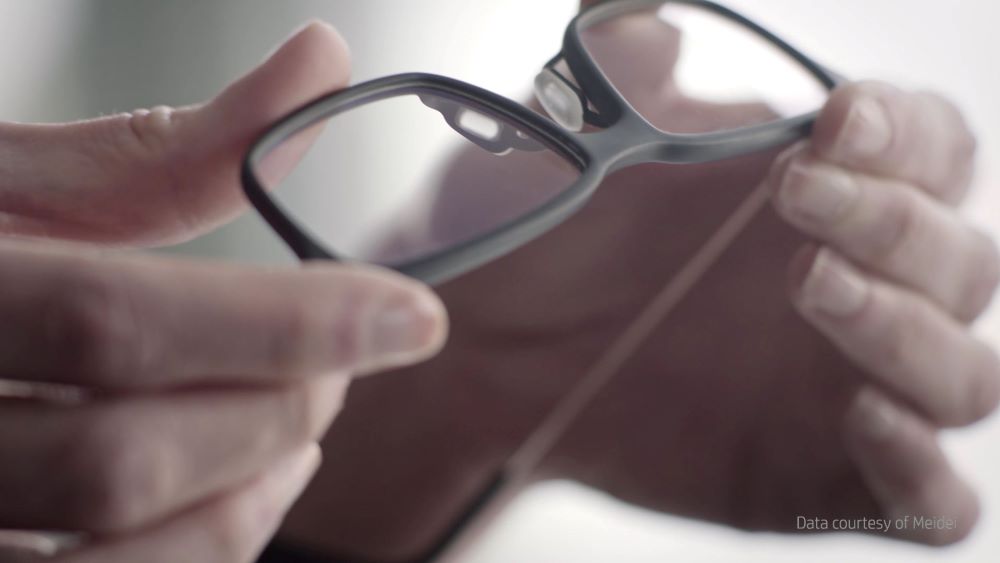
3. Sustainable Solutions for Consumer Goods
Sustainability is a growing concern for consumers and companies alike. More manufacturers adopt environmental, sustainability, and governance (ESG) measures, which means they are actively seeking environmentally friendly alternatives.
Some traditional, subtractive manufacturing processes result in large amounts of waste when it comes to continuous prototyping. Not only does this contribute to landfills, it also costs the company money. 3D printing, on the other hand, is an additive process. Material is only used where needed.
In the consumer goods sector, companies can leverage 3D printing to produce personalized items like eyewear, sporting goods, jewelry, and wearables with less environmental impact.
Manufacturers can also produce goods on demand. They don’t need to produce and store large inventories, which may or may not be cleared out.

4. Complex Components for Aerospace
The aerospace industry is one of the most advanced adopters of 3D printing technology. Manufacturers work with complex geometries that are difficult — even impossible — to produce using traditional methods.
Turbine blades, fuel nozzles, rocket injectors, and other parts need to be both lightweight and highly durable.
3D printing allows manufacturers to create parts with intricate internal structures to boost performance without adding excess weight. This can be a game-changer — reducing weight leads to improved fuel efficiency and lower operational costs.
Aerospace manufacturers also incorporate metal 3D printing in their processes, which can produce lightweight, high-strength components that withstand extreme conditions.
Additionally, 3D printing enables rapid prototyping. Engineers can test and refine designs fast.
5. Metal 3D Printing for Automotive
Metal 3D printing is fast becoming a mainstay in the automotive industry. Traditional automotive manufacturing involves processes like casting or forging.
These require huge amounts of time plus hefty investments in molds and tools. Metal 3D printing removes these barriers, so manufacturers can build high-performance components faster and cheaper.
Like with the aerospace industry, one of the main advantages of metal 3D printing is its ability to develop lightweight, high-strength parts that can endure harsh conditions. Automotive manufacturers can 3D-print custom components optimized for both weight and strength.
Vehicles perform better while using less fuel. This improves product quality while further strengthening the company’s sustainability initiatives.
Transform Your Manufacturing with 3D Printing
3D printing is no longer just a tool for rapid prototyping. It’s a business option for manufacturers — one that can produce complex, custom parts faster, with greater efficiency, and with a smaller carbon footprint.
Discover how you can reap the benefits of 3D printing by downloading our ultimate guide, Unlock the Power of 3D Printing.
Ready to Get Started? Learn More About A3D Manufacturing as Your MaaS Solution
We help businesses like yours unlock the full potential of next-generation 3D printing and traditional manufacturing. Our on-demand production services are backed by expert guidance and proven workflows. You can focus on innovation and customer experience excellence, knowing the manufacturing side is taken care of.
Get a quote or reach out to the team behind A3D Manufacturing today. Together, we can explore how our MaaS solution can fuel the next phase of your business growth.